Technology in Early Childhood Education – Part 2
In the ever-evolving landscape of education, integrated hybrid learning has transformed the traditional classroom model, bringing forth a new era of educational possibilities. As our children embark on a journey that seamlessly blends in-person and online learning experiences, it becomes imperative for parents and caregivers to play a pivotal role in supporting this transition. The synergy between home and school is more critical than ever, and this blog aims to be your guiding light in navigating the complexities of integrated hybrid learning.
As we collectively embrace the opportunities and challenges this educational paradigm shift presents, parents and caregivers must be equipped with the knowledge and tools necessary to foster a conducive learning environment. From understanding the digital tools employed in classrooms to fostering effective communication with educators, this blog will delve into the various facets of integrated hybrid learning and provide actionable insights to empower parents and caregivers.
Empowering Parents And Caregivers In Supporting Integrated Hybrid Learning:
- Active Participation In Inquiry-Based Experiences: Parents and caregivers can actively engage in inquiry-based experiences with their children, encouraging curiosity and exploration. It involves hands-on activities beyond technology, fostering a holistic learning environment.
- Incorporation Of Technology In Joint Activities: While technology is a valuable tool, parents and caregivers should integrate it judiciously into joint learning activities. It includes using touchscreen tablets in pairs or small groups, aligning with a learning-centres structure similar to other learning tools like block corners or water tables.
- Advanced Vocabulary And Open-Ended Questions: Encouraging advanced vocabulary and posing open-ended questions during hands-on activities, whether involving technology or not, can enhance early literacy scores. This approach stimulates critical thinking and language development in children.
- Creating A Balanced Learning Environment: Emphasizing the importance of a balanced learning environment that combines technology with other hands-on experiences. It helps avoid an overreliance on a 1:1 device-to-child approach and ensures a more comprehensive and effective learning experience.
- Supporting Learning-Center Structures: Parents and caregivers can align their support with the learning-center structure, recognizing that technologies, like iPad Chromebooks or tablets, are most effective when integrated into small groups. This approach promotes collaboration, sharing, and diverse interactions among children.
- Understanding Technology As A Facilitator, Not A Replacement: Acknowledging that technology facilitates the learning process but should not replace the essential role of human interaction and hands-on experiences. Encouraging a balanced approach where technology enhances, rather than substitutes, traditional learning methods.
- Staying Informed And Involved: Keeping abreast of the latest developments in educational technology and understanding how these tools can be effectively incorporated into hybrid learning. Engaging in children’s learning activities fosters a supportive and collaborative academic environment.
- Encouraging Collaboration And Communication: Facilitating opportunities for children to collaborate and communicate using technology. It can include joint exploration of educational apps or games, encouraging discussion, and sharing insights.
- Modelling Lifelong Learning: Demonstrating a commitment to lifelong learning by engaging in activities that incorporate technology responsibly. Modelling positive attitudes toward education reinforces the importance of continuous curiosity and adaptation.
- Promoting a Positive Attitude Toward Learning: Instilling a positive attitude toward learning, emphasizing that technology is a valuable tool within a broader spectrum of learning experiences. Encouraging a mindset that values exploration, critical thinking, and the joy of discovery.
Recognizing The Essential Role Of Teachers In Early Childhood Learning:
- Crucial Involvement In Children’s Learning: Teachers play a critical role in young children’s educational journey. Their guidance and instructional strategies significantly impact children’s engagement and comprehension of concepts.
- High-Quality Resources For Early Childhood Education: Access to high-quality resources ensures that all students can achieve standards-based learning outcomes. Teachers need reliable tools and materials to create an engaging and effective learning environment in a rapidly evolving educational landscape.
- Addressing Underestimation Of Children’s Abilities: Addressing the common misconception that underestimates what young children can learn is crucial. Teachers should be empowered to allow children to explore numbers, patterns, and relationships and engage with scientific phenomena. It sets the foundation for later advanced concept learning.
- Promoting Interactive Learning Experiences: Encouraging teachers to design interactive learning experiences that enable children to make sense of concepts of all subjects. It involves creating opportunities for hands-on exploration, experimentation, and observation.
- Fostering A Positive Attitude Towards Learning: Teachers play an indispensable role in shaping children’s attitudes toward learning and academics. By fostering a positive and inclusive environment, teachers can instill a love for knowledge and curiosity and make them lifelong learners.
- Collaboration And Support: Creating a collaborative and supportive community among educators is essential. Sharing best practices, resources, and experiences can enhance teaching effectiveness in early childhood education.
- Advocacy For Technology In Education: Teachers can advocate for technology education, promoting its importance and advocating for the necessary support, resources, and recognition within the educational system. It ensures a holistic approach to early childhood learning that benefits teachers and students.
Empowering Collaborative Pedagogical Design For iPad And Tablets In Early Childhood Learning:
- Facilitate Collaborative Workshops: Encourage teachers to participate in collaborative workshops where they can collectively design pedagogical repertoires for using tablets. These workshops should provide a platform for sharing ideas, experiences, and effective practices in integrating tablets into early childhood education.
- Recognition Of Multimodal Ipad Use: Emphasize the multimodal quality of iPad use in educational centres. Acknowledge that iPads and tablets offer diverse modes of engagement, including visual, auditory, and interactive elements. Teachers should be encouraged to explore and integrate these multimodal features in their teaching practices.
- Demonstrate Transformative iPad Use: Illustrate the transformative nature of tablet use by showcasing examples where tablets modify or redefine current teaching practices. Highlight instances where tablets enhance learning experiences, foster collaboration, and provide new avenues for exploring concepts.
- Provide Case Studies And Exemplars: Share case studies and examples that showcase successful implementations of tablet use in early childhood education. These examples can inspire teachers, illustrating the positive impact of integrating tablets into their pedagogical approaches.
- Promote Reflective Practices: Encourage teachers to engage in reflective practices as they explore and implement iPad-based learning activities. Reflection allows educators to assess the effectiveness of their approaches, make adjustments, and continually refine their use of iPads and tablets in early childhood education.
- Create Collaborative Learning Communities: Establish collaborative learning communities among teachers to regularly exchange insights, challenges, and strategies for tablet use in early childhood education. These communities provide ongoing support and foster a culture of shared learning.
- Professional Development Opportunities: Provide continuous professional development opportunities for iPad and tablet integration in early childhood education. Workshops, seminars, and online courses can help educators stay informed about emerging trends, effective practices, and innovative tablet-use approaches.
- Encourage Experimentation And Innovation: Foster a culture of experimentation and innovation among teachers. Encourage them to explore creative ways of using tablets to engage students in early childhood learning, allowing for a sense of ownership and autonomy in their pedagogical practices.
- Collaborative Lesson Planning: Encourage collaborative lesson planning sessions where teachers collectively design early childhood lessons that leverage iPads and tablets’ interactive and multimedia capabilities. This collaborative approach ensures a diverse range of perspectives and ideas.
- Advocate for Multimodal Learning: Advocate for the importance of multimodal learning in developing skills required in today’s and tomorrow’s society. Highlight how tablet use can facilitate diverse learning modalities, catering to different learning styles and enhancing the acquisition of critical skills.
Digital technologies are crucial in assisting early childhood educators with planning and documentation processes. Educators can conduct consistent and systematic observations of children’s learning and development by carefully selecting tools and applications incorporating progress monitoring features. This approach contributes to a more efficient and organized assessment of children’s progress.
Various technology tools, including digital cameras, digital audio devices, scanners, and electronic portfolios, can be employed to systematically monitor and document children’s progress. These tools enable educators to create permanent records of children’s work, offering a comprehensive overview of their developmental journey.
Furthermore, various commercial web-based software supports the planning and documentation process in early childhood education settings. These digital resources provide educators with a streamlined approach to documentation, making the entire process more accessible and manageable.
Recent research indicates a growing trend among educators to adopt digital resources for planning and documentation. Technology in early childhood education settings enhances efficiency and creates a comprehensive and dynamic record of each child’s learning and developmental milestones.
Integrating emerging technologies into early childhood education holds great potential for transforming and improving the learning landscape. This comprehensive examination of the role of emerging technologies in early childhood education addresses several key areas and outlines potential challenges and future directions. Here are the main points covered:
The discussion emphasizes the importance of inclusivity, diversity, and equity in early childhood education. Inequalities in early childhood education can negatively impact career prospects, and emerging technologies, such as virtual reality (VR) and coding, are explored as tools to encourage underrepresented groups, particularly females, to participate in classroom activities.
- Interdisciplinary Learning: The special issue advocates using emerging technologies like VR and AI to create a conducive environment for interdisciplinary early childhood learning. These technologies enable students to explore digital arts, expand STEM to STEAM (including arts), and incorporate knowledge from various disciplines, making education more comprehensive.
- Rethinking Learning Outcomes: The authors propose reevaluating learning outcomes in early childhood education due to the impact of emerging technologies. The focus is on developing computational thinking, AI literacy, creativity, leadership, and collaborative skills. The evolving nature of the workforce requires an adaptation of educational goals.
- Challenges And Issues: Several challenges and issues associated with integrating emerging technologies are highlighted. These include the potential for widening the digital divide, prerequisite skills in computational thinking and digital literacy, technical and health concerns, and the importance of providing safe learning environments.
- Future Research Directions: The special issue identifies areas for future research, including the exploration of safe learning environments when employing emerging technologies, the development of teacher professional learning programs for using these technologies, and the need for theoretical perspectives to support research in this field.
Overall, the discussion emphasizes the transformative potential of emerging technologies in early childhood education and underscores the importance of addressing challenges to ensure equitable access and positive learning outcomes. Researchers and educators are encouraged to consider the ethical, privacy, and psychological implications of incorporating emerging technologies into education while envisioning a future where these technologies contribute to a vibrant and compelling early childhood learning environment.
Integrating technology into early childhood education is crucial in today’s digital age. This comprehensive exploration highlights the various ways technology can enhance and transform learning:
Online Interactive Learning: Online learning, particularly platforms like Apple Education, G-Suite for Education and Google Classroom, has become integral in broadening the reach of early childhood education.
Collaborative tools allow students to share information, extract critical ideas, and organize their understanding.
Simulation: Simulation tools provide opportunities for students to manipulate virtual and actual environments, aiding in developing STEM understanding.
Simulations are particularly valuable when actual equipment is challenging to obtain or might be too expensive or dangerous for a school setting.
Augmented Reality and Virtual Reality:
- Augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) offer immersive learning experiences that can revolutionize early childhood education.
- Companies like Lifelique and Labster VR provide 3D models and realistic lab experiences, making science learning visual, hands-on, and interactive.
- Unity Technologies’ AR/VR applications and platforms like NeoTrie VR contribute to creating engaging and innovative learning environments.
- Gaming:
- Video games facilitate participatory learning activities, critical thinking, problem-solving, and active engagement.
- As instructional tools.
- Well-designed video games are highly engaging and can harness students’ interest, making them a natural tool for teaching coding and computer skills.
Applications
- Integrating technology, including online interactive learning, simulation, AR, VR, and gaming, enhances STEM learning and student success.
- Examples of effective applications include Apple Education and Google’s G Suite and Classroom, simulation tools, immersive technologies like AR and VR, and educational games.
Empowering Teaching, Planning, and Assessing-
Digital Documentation:
- New technologies, including digital platforms, must be used for planning, observations, assessments, and developing children’s portfolios.
- Educators must utilize critical reflections within these platforms, enhancing documentation quality.
Communication with Families:
- Technology must facilitate feedback from families and incorporate their views into curriculum plans.
- Policies and philosophies must be displayed through screens/tablets, and communication occurred through various channels, such as email and social media.
Educators’ Training and Collaboration:
- Educators must attend webinars, collaborate, and use technology to document spontaneous learning and reflections.
- Technology, like mind maps, must support educators in showcasing the progression of projects and learning for children of all ages.
Children’s Learning:
- Quality Improvement Plans (QIPs) must emphasize using technology for implementing STEM in early childhood, accessing child-appropriate websites, and supporting research through devices like iPads.
- Educators must recognize the role of technology in fostering innovative thinking and problem-solving skills in children.
Collaborative Partnerships With Families And Communities
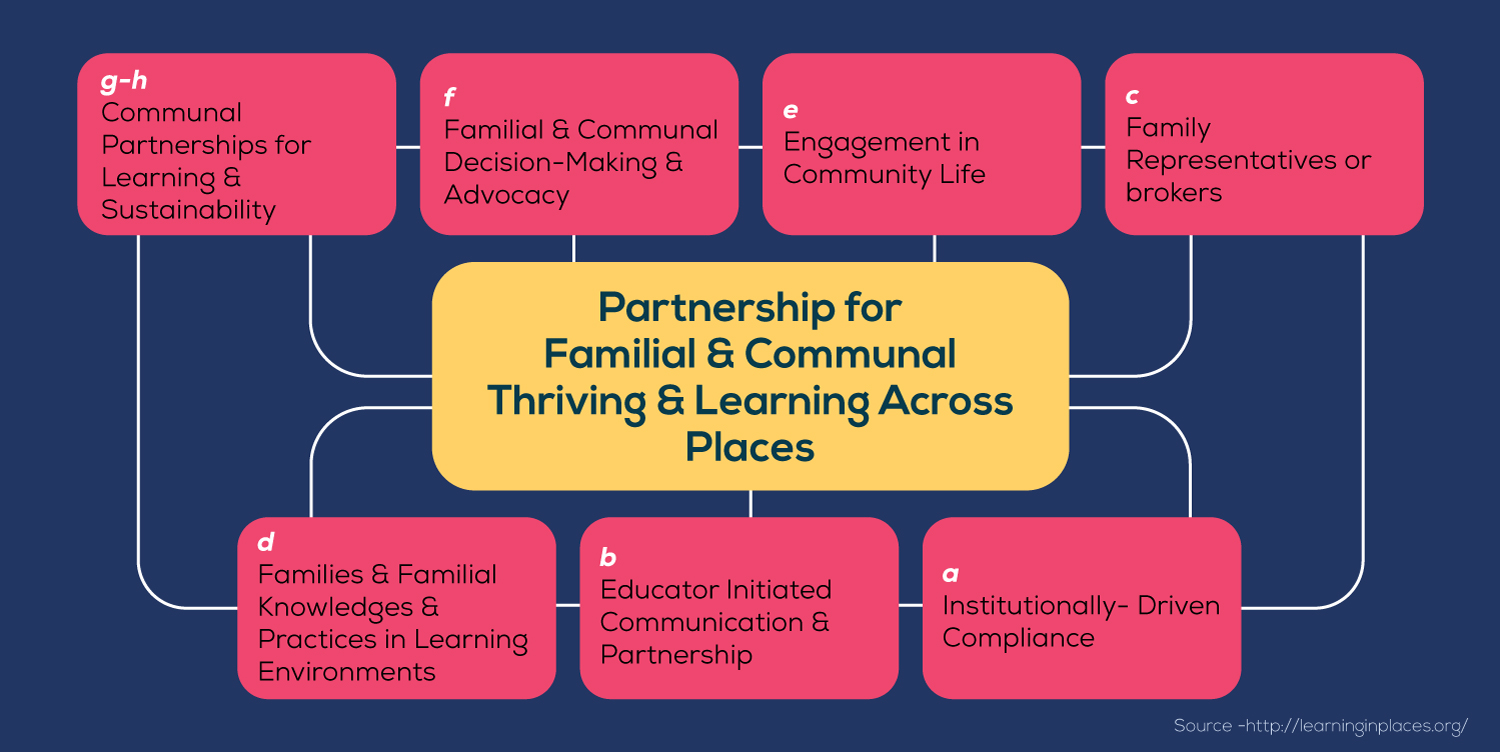
Communication:
- Various digital media, including social media, online tools/platforms, emails, and websites, must be employed to enhance relationships between ECEC settings and families.
- Digital communication strategies must be emphasized to strengthen collaborations and partnerships.
Access and Sharing of Information:
- Digital media must facilitate the distribution of enriching information, event notifications, and cultural awareness initiatives.
- Technology must play a role in the induction process for new families, ensuring a smooth transition and effective communication.
Constructive Feedback and Input:
- Families must be provided opportunities through digital media to contribute to children’s e-portfolios and provide feedback on decision-making and policies.
Improvement of Advertising and Community Relationships:
- Settings must be utilized technology to enhance their presence in the community, advertise events, and foster community involvement.
Communication with Families and Educators:
Technological media and processes must be adopted to share information with families, update them on changes, and obtain feedback.
- Technology facilitates communication and collaboration among educators, supporting effective leadership and management.
Acknowledging The Role Of Teachers As Mediators:
- Recognize the crucial role that teachers play as mediators of digital experiences. Guide adults on how to use digital resources effectively, both in terms of content and learning goals.
Integration Of Adult Needs Into Content:
- Design digital resources that cater to the needs of both adults and children. Include models of dialogue between adults and children, emphasizing effective communication strategies such as asking clarifying questions or restating opinions.
Interpreting And Applying Educational Standards:
- Offer resources that assist teachers in interpreting and applying educational standards relevant to STEM learning. It includes providing support for aligning teaching practices with standards and benchmarks.
Professional Development Opportunities
- Provide professional development opportunities tailored to the unique needs of early childhood professionals. These opportunities should focus on enhancing STEM pedagogy and content knowledge, considering early learning settings’ specific challenges and requirements.
Contextualized Support For Different Communities:
- Understand and address the unique needs of early childhood educators in different communities. For instance, educators in lower-income communities may require financial support for professional development and access to technology infrastructure.
Collaboration for Research and Practice:
- Encourage research-practice collaboration models to improve student learning of STEM in the early grades. Interactive mobile technologies can be utilized for such collaborations, fostering innovative approaches to STEM education.
Inclusivity in Resource Development:
- Ensure that resource development considers early childhood educators’ diverse backgrounds, experiences, and resources. Strive for inclusivity in the design and implementation of STEM educational initiatives.
A comprehensive approach to supporting early childhood educators involves:
- Understanding their unique needs.
- Providing targeted professional development.
- Leveraging technology in ways that enhance both adult and child learning experiences.
Additionally, initiatives should be flexible and inclusive, considering the diverse contexts in which early childhood educators operate.
Conclusions and Future Recommendations:
- Students in the 21st century, often called “digital natives,” require different learning goals and teaching approaches due to their immersion in technology.
- Technology is no longer an option but a fundamental literacy, and its integration should be designed with teachers and students in mind.
- Educational leaders and administrators face the challenge of creating accessible online learning opportunities while providing adequate support.
- Careful evaluation of digital resources for curriculum fit, effectiveness, and alignment with best practices is essential.
- The role of teachers as mediators of digital experiences is crucial, and efforts should be made to ensure widespread access to technology in early childhood education.
A comprehensive approach to supporting early childhood educators involves:
- Understanding their unique needs.
- Providing targeted professional development.
- Leveraging technology in ways that enhance both adult and child learning experiences.
Additionally, initiatives should be flexible and inclusive, considering the diverse contexts in which early childhood educators operate can transform learning experiences, making them more engaging, immersive, and aligned with the needs of 21st-century learners.
